What is the scabies in dogs
Scabies in dogs is an inflammatory disease associated with damage to the body by microscopic scabies mites. There are several varieties that differ in the type of pathogen and symptoms. Severe itching and associated symptoms cause serious discomfort to the pet, and if left untreated, scabies is dangerous for the development of secondary infections. The ability to identify the signs of the disease and the timely appeal to the veterinarian greatly facilitate the process of healing the pet
Symptoms and varieties
The main symptom of scabies is increasing itching, which is associated with irritation of the nerve receptors of the skin, damaged by mites. Other manifestations of the disease will vary somewhat depending on the type of pathogen
cheiletiosis
Another name for the disease is wandering or pityriasis scabies - one of the contagious varieties. Cheyletiellayasguri mites most often settle on the surface of the skin of the neck, ears, (sometimes back), feeding on tissue fluid and dying cells. Typical symptoms
severe inflammation of the affected areas
hair loss, often in clumps
the appearance of a rash or ulcers, which eventually transform into hard scales and crusts
Sarcoptic mange
The popular name for the disease is pruritic scabies. In this case, areas with short hair are most often affected: the nose, superciliary regions, ears, joints of the limbs. The Sarcoptescanis mite penetrates into the deep subcutaneous layers, where it gnaws passages for laying eggs. The first symptom of sarcoptic mange is small dots, which after 10-14 days turn into small itchy sores. Such scabies resembles a flea infestation with the corresponding characteristic biting. In addition, there is
restless dog behavior due to parasite bites
combing the affected areas to the blood, followed by the formation of crusts and scabs
"ear reflex", when, when touching the auricle, the dog immediately tries to scratch the affected ear behind the paw
hair loss in the lesions
possible formation of a rash, abscesses
Otodectosis
The disease is caused by the mite Otodectescynotis, which infects the inner surface of the ears, which is why it is also called ear scabies. It is transmitted from one animal to another through prolonged contact and is most common in long-eared dog breeds. The tick feeds on the blood of the animal and, as it matures, becomes stronger in the upper layers of the skin, causing severe itching. Specific symptoms: brown sticky coating in the auricle (mites waste)
frequent shaking of the head and inclination towards the affected ear
constant attempts to rub your head against the owner and surrounding objects
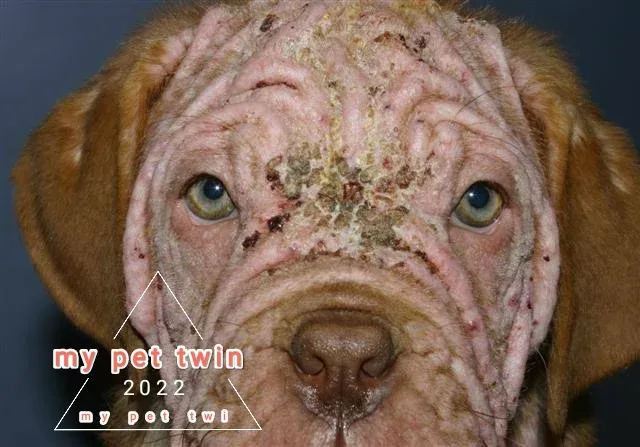
Notoedrosis
The mite that causes scabies settles in the deep layers of the dog's epidermis. It is able to move easily, therefore it quickly affects surrounding animals, especially young individuals. The following symptoms indicate infection
persistent itching and irritation
small bubbles and nodules on the face, ears, back, abdomen
folding of the affected areas of the skin
hair loss
Disease danger
Scabies mites are aggressive parasites that cannot be eliminated without medical intervention. Prolonged stay in the body causes more damage to the body. Among the negative consequences
General intoxication. With an increase in the number of ticks, the volume of their waste products increases, which enter the bloodstream and cause toxic reactions
Growth of pathogenic microflora. The affected inflamed areas eventually become covered with a crust, under which putrefactive microorganisms actively develop
infectious diseases. Severe itching leads to deep scratching of the inflamed areas, and a violation of the integrity of the skin creates a favorable environment for the development of infections
Weakened immunity. Due to constant itching, the animal becomes restless, loses mood and appetite. As a result, the body is exhausted, which leads to a weakening of the immune system
Diagnosis of the disease
Despite the fact that on the Internet, you can see numerous photos of scabies in dogs, to make an accurate diagnosis, you should examine your pet at the veterinarian. But first, the owner should pay attention to
pet behavior, frequency and area of scratching
the condition of the skin and the presence of inflammatory reactions on the skin
appearance and degree of hair loss
Due to the microscopic size of the tick, you should not try to examine it on the body. one of the possible options is to feel the presence of the smallest tubercles on the skin with your fingertips. In veterinary clinics, an ultraviolet lamp is used, in the light of which traces of vital activity of parasites are clearly visible. But the main diagnostic method is scraping from the affected area, which is placed in a glycerin solution and studied under a microscope
Scabies treatment
Treatment of scabies is carried out at home with the obligatory isolation of the dog from other animals and people. But first it is important to contact a specialist in order to accurately establish the causative agent of the disease and receive the necessary appointments. Regardless of the type of scabies in a dog, treatment is selected in two directions
ridding the animal of parasites
elimination of accompanying symptoms
For these purposes, means of external and internal use are used. The treatment regimen is determined taking into account the type of pathogen, the degree of damage to the body and the general condition of the dog
Treatment for scabies includes: Removal of hair from affected areas of the body
Bathing with anti-seborrheic shampoo. Puppies can only treat the affected areas, adults are bathed completely
The use of antiparasitic agents (for injections and external use) is the main direction of treatment. Prescribed drugs based on selamectin, ivermectin, imidacloprid and moxidectin (Stronghold, Milbemax, Lawyer, Ivomek, Ivermectin). Aerosol products will be convenient to use - Cydem, Demizon, Tsiodrin, Akrodex. When using external acaricidal preparations, care must be taken that the dog does not lick them off. You can use a special collar or muzzle. If there are other dogs or cats in the house, preventive treatment is carried out with external agents used for an infected pet
Treatment with oil solutions (with the formation of a large number of scabs). 4% colloidal sulfur or 1% TAP (tissue plasminogen activator) is used, which are mixed with vaseline or sunflower oil and heated to 30-35°C before use
Removing crusts. They can be softened with warm soapy water or 0.2% caustic soda solution
Treatment of household items (through boiling or using chlorophos) and housing in general (steam or insecticides)
As auxiliary means, combinations of tar with petroleum jelly (1 to 9) and creolin with green soap and alcohol (1/1/10) are considered the most effective
In addition, it is possible to use glucocorticoids (Dexamethasone, Clobetasol, Dexamethasone) with increased itching, preparations with sulfur to restore the coat (Dekta, Demos), sedatives and antibiotics
The duration of treatment is determined by the veterinarian and in advanced cases can take up to 8 weeks. One of the mistakes in the treatment of scabies is busting with antiparasitic drugs. If the dog continues to itch beyond the standard course (usually 4 weeks), do not re-treat. Persistence of itching for 1 week is considered a normal body response to dead mites. The use of new drugs can provoke increased itching and the development of allergic dermatitis
Read more
What shape of the largest dog in the world
Causes lead to the death of parrot
If you want to buy a British Shorthair cat, here is some information